Trip Overview
Pisang Peak climbing is the most popular peak among the trekking peaks in Nepal offering a good scope for exploration and peak climbing experience in the Himalayas of Nepal. Although Pisang Peak falls among one of the non-expedition peaks in Nepal, this peak is popular among climbers as one of the Adventure trekking peaks in Nepal. Pisang peak rises opposite of Annapurna II (7937) and lies in between the famous Mount Annapurna I and Mt. Manaslu. The Pisang peak climbing adventure can be combined with the world-famous Annapurna Circuit trekking.
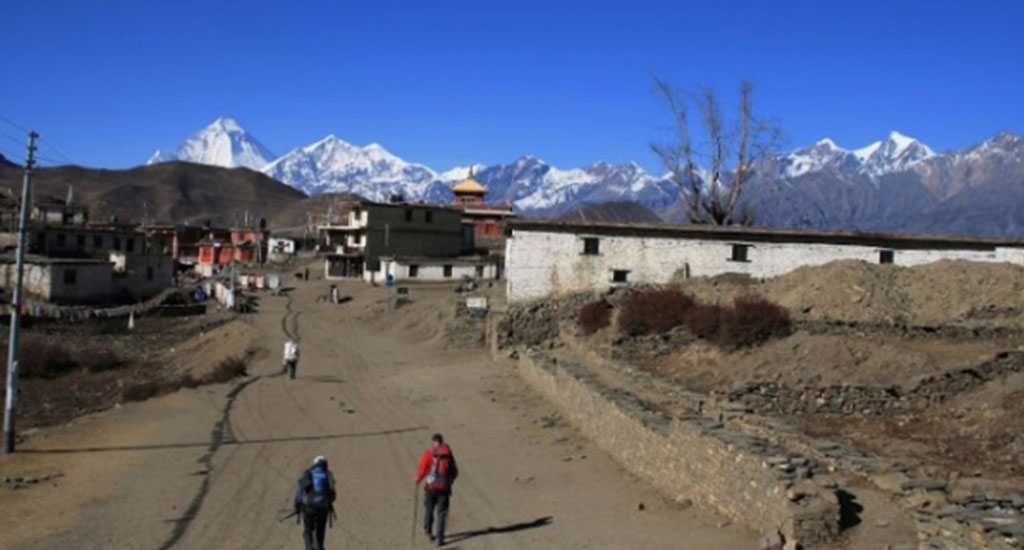
Pisang Peak Climbers have to pass through the Pisang village and yak pastures with a uniform rise in the slope of ice and snow to the final summit of Pisang. Climbing the Pisang peak is an easy climbing adventure as this peak is one of the easiest climbing peaks in Nepal.
Pisang peak climbing offers close-up views of the Annapurna range (40 miles between the two river valleys contain twelve 7000 m peaks and many more above the 6000m marks).
Pisang Peak Climbing Cost
18 Days Pisang Peak Climbing costs USD 2550 per person. The cost includes the cost of transportation, meals, and other facilities like Tents, camping, Hight altitude Tents, and others as mentioned in the Includes section. Pisang Peak climb can be done both in Spring and Autumn however we recommend you to ascend during the Spring season. If you have a big group willing to climb Pisang Peak and any other trekking peaks in Nepal, please contact us, we can offer you Group Discounts too.
Best time for Pisang peak Climbing
Pisang Peak climbing is best during the months of March to May and September to December. Pisang peak can be climbed both in Spring and Autumn seasons. However, we highly recommend you to plan climbing Pisang peak during the Spring season as the weather remains steady and clear during these months.
How challenging is Pisang peak climbing?
Pisang peak is challenging for beginners, however this peak can be climbed by climbers of all levels. Climbing Pisang peak involves several difficulties, like altitude sickness, challenging routes, weather, rapid temperature changes and type of accommodation during the climbing and expedition period.
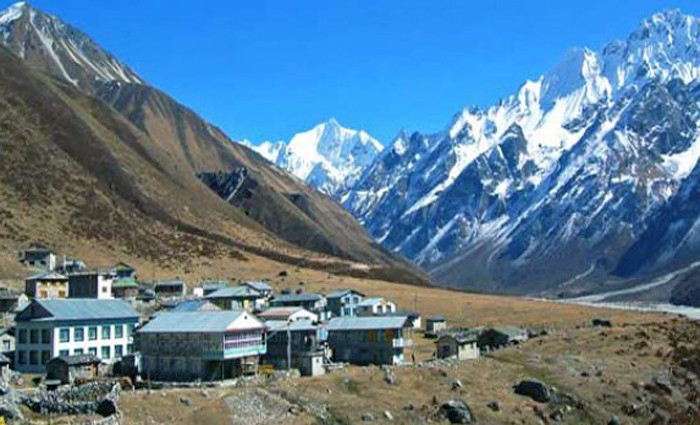




 Annapurna II can be seen to the south and you are now behind the main Himalaya peaks in their rain shadow area. After crossing a series of wooden cantilever bridges you enter a spruce and fir forest that eventually gives way to a pine forest. After days in the gorge the forests provide a welcome change. Crossing the river to its left bank you reach your lodge at the village of Pisang. You may want to visit the village before dinner. Camp
Annapurna II can be seen to the south and you are now behind the main Himalaya peaks in their rain shadow area. After crossing a series of wooden cantilever bridges you enter a spruce and fir forest that eventually gives way to a pine forest. After days in the gorge the forests provide a welcome change. Crossing the river to its left bank you reach your lodge at the village of Pisang. You may want to visit the village before dinner. Camp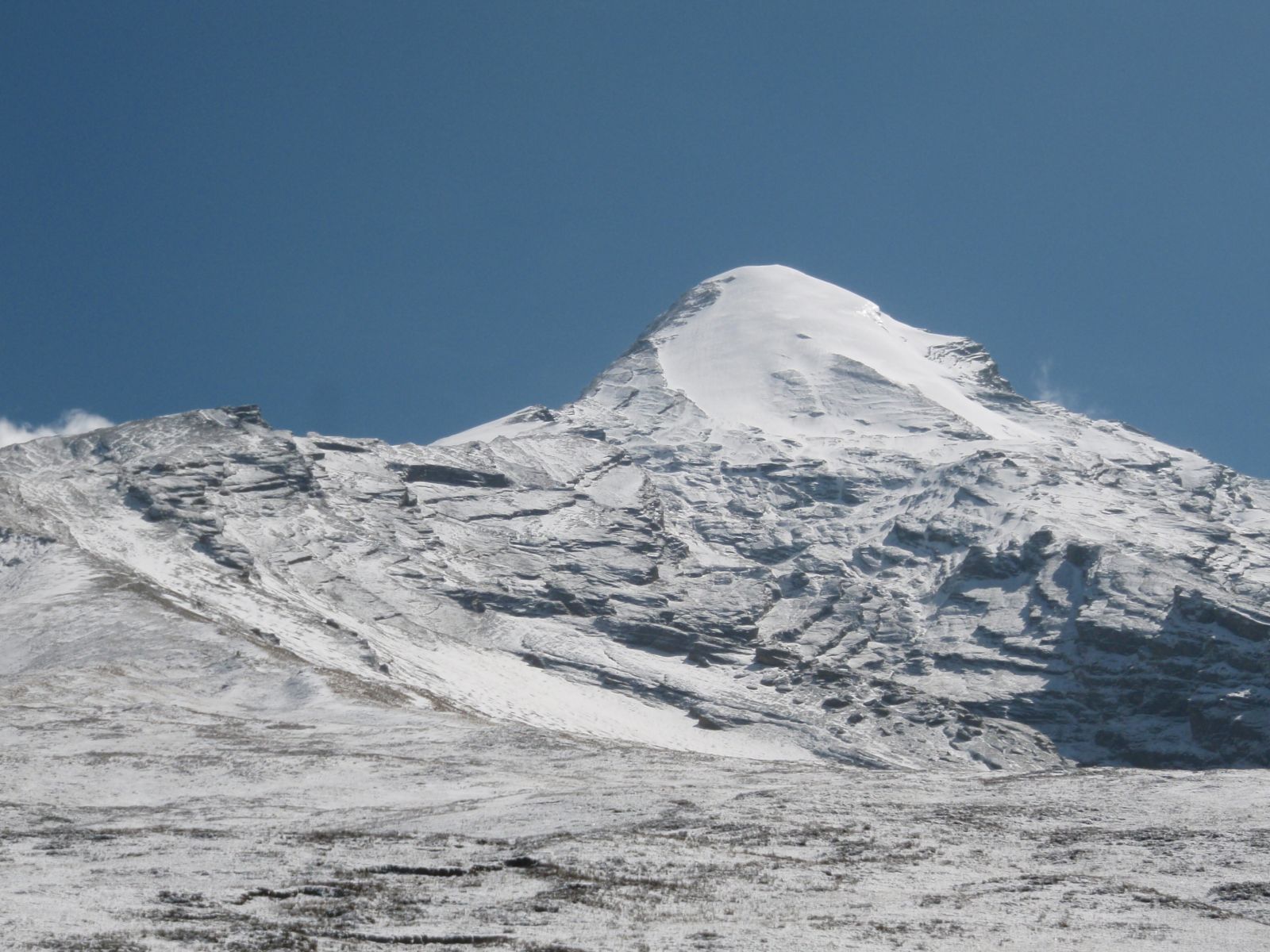
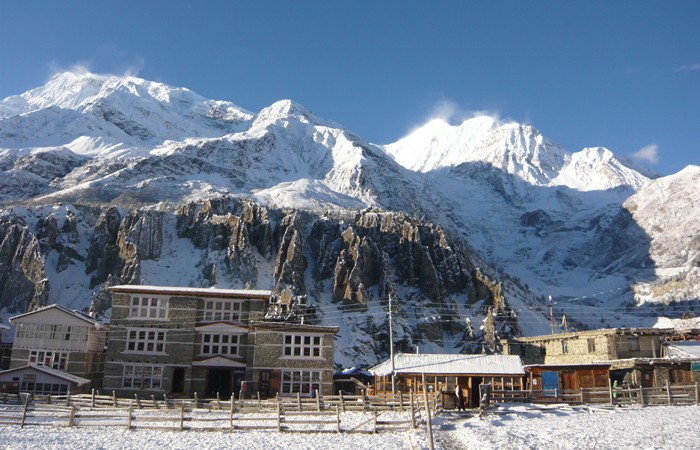

 Continue through pastures, which eventually give way to high arid desert at Phedi, at the base of Thorung La. Camp
Continue through pastures, which eventually give way to high arid desert at Phedi, at the base of Thorung La. Camp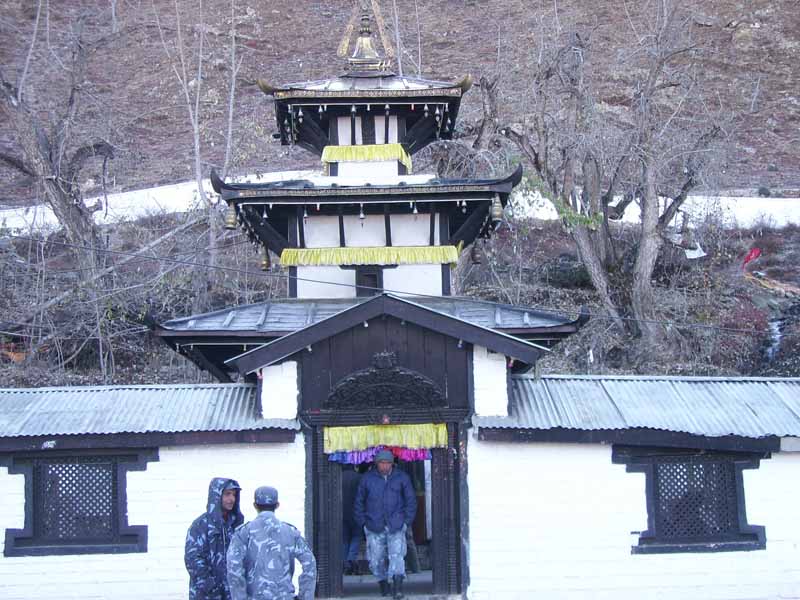 Muktinath is a sacred pilgrimage site to both Hindus and Buddhists who flock there annually for their respective festivals. A rest day here allows you the opportunity to explore the area and the ancient shrines. Of particular interest is the temple of the Hindu God Vishnu and the one hundred and eight waterspouts where devotees bathe. From Muktinath there are beautiful views of Mt. Dhaulagiri (8167m). Camp
Muktinath is a sacred pilgrimage site to both Hindus and Buddhists who flock there annually for their respective festivals. A rest day here allows you the opportunity to explore the area and the ancient shrines. Of particular interest is the temple of the Hindu God Vishnu and the one hundred and eight waterspouts where devotees bathe. From Muktinath there are beautiful views of Mt. Dhaulagiri (8167m). Camp